Some time back I came across the following quote in The 80/20 Principle : The Secret of Achieving More With Less by Richard Koch, which I’ve been pondering ever since for its implications for knowledge work and knowledge workers:
There are only four types of officer. First, there are the lazy, stupid ones. Leave them alone, they do no harm…Second, there are the hard- working, intelligent ones. They make excellent staff officers, ensuring that every detail is properly considered. Third, there are the hard- working, stupid ones. These people are a menace and must be fired at once. They create irrelevant work for everybody. Finally, there are the intelligent, lazy ones. They are suited for the highest office.
General Erich Von Manstein (1887-1973) on the German Officer Corps
You can also map this quote into the following matrix representation:
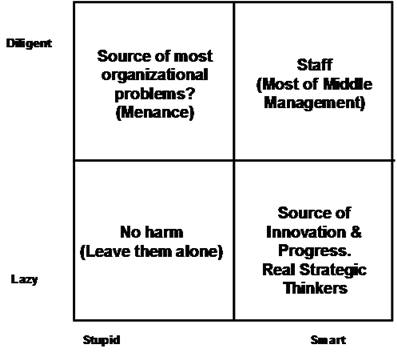
One implication certainly is that you want to keep the average IQ up in your organization (setting aside all the limits on accurately measuring or assessing something as complex as intelligence for the moment). My own theory is that it also suggests that you want to keep your organization relatively small to maintain some degree of control over that average IQ. You may also want to keep the distribution of IQ in your organization as tight as possible.
The laziness/diligence dimension is the more interesting of the two in the context of knowledge work organizations. Common organizational practice is biased in favor of diligence, while laziness doesn’t get the respect it deserves. Granted, the appearance of blogs such as Slacker Manager is a hopeful sign, as is the recent spate of activity and commentary around the importance of innovation and creative thinking for knowledge based organizations. But our Puritan/Calvinist heritage still dominates reward and evaluation systems. Regardless of the actual importance of thought and reflection to long-term organizational success, you are better off looking busy than looking like you are thinking. Even organizations that exist to promote reflective thought (e.g., universities, research institutes, think tanks) fall into the trap of encouraging diligence at the expense of reflection/laziness.
I don’t yet have a fully workable solution to the problem of carving out sufficient and appropriate time for thinking and reflection. More often than not, it gets relegated to plane-time, travel-time, and after-hours time; essentially bypassing the organizational problem. I’ve found that mind-mapping, either by hand on on the computer, is one form of thinking that can be done in public without triggering unwanted negative perceptions. Setting aside time to maintain some form of journal (whether in the form of a blog or more private diary) is another thinking/reflecting discipline that is both productive and not immediately threatening to the activity police.
Here are some questions I think are worth exploring in this context.
- What alternate terms than diligence and laziness could we use to better frame the issue?
- How important is it to carve out times and places to engage in visible laziness within organizations?
- Is this a problem that needs to be solved at the organizational level? For which types of organization?
- What barriers to innovation, if any, does a bias toward diligence create?
Any takers?
Hans Rosling, professor of public health, speaker extraordinaire, software entrepreneur and one of the best illustrators of fact-based research and policy discussions I have ever seen, is now available in English from the TED conference.



